Combination of Resistor
SERIES CIRCUIT
यदि दो या दो से अधिक घटक श्रृंखला में जुड़े होते हैं तो उनके अंत में धारा (current) समान होता है।
सीरीज़ सर्किट को कभी-कभी Current-coupled या Daisy chain-coupled कहा जाता है।
एक श्रृंखला सर्किट की सिद्धांत विशेषता यह है कि इसमें केवल एक ही पथ है जिसमें धारा प्रवाह हो सकता है। किसी भी बिंदु पर एक श्रृंखला सर्किट खोलना या तोड़ना पूरे सर्किट को "खोलने" या संचालन बंद कर देता है। उदाहरण के लिए, यदि क्रिसमस के पेड़ की रोशनी की पुरानी शैली की स्ट्रिंग में प्रकाश बल्बों में से एक भी जलता है या हटा दिया जाता है, तो बल्ब बदल जाने तक पूरी स्ट्रिंग निष्क्रिय हो जाती है।
Voltage
In a series circuit the voltage is addition of all the voltage elements.

CUrrent

👉 In a series circuit, the current is the same for all of the elements.
Resistors
The total resistance of resistors in series is equal to the sum of their individual resistances:-
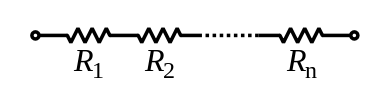

Inductors
Inductors follow the same law, in that the total inductance of non-coupled inductors in series is equal to the sum of their individual inductances:


Capacitors
Capacitors follow the same law using the reciprocals. The total capacitance of capacitors in series is equal to the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of their individual capacitances:
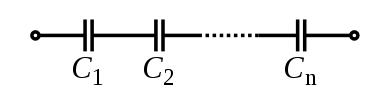

PARALLEL CIRCUIT
यदि दो या दो से अधिक घटक समानांतर में जुड़े होते हैं तो उनके अंत में Potential difference (वोल्टेज) समान होता है। घटकों में संभावित मतभेद समानता में समान हैं, और उनके समान समान ध्रुवीयताएं भी हैं। समान वोल्टेज समानांतर में जुड़े सभी सर्किट घटकों पर लागू होता है। Kirchhoff's Law के अनुसार, कुल वर्तमान विशिष्ट घटकों के माध्यम से धाराओं का योग है।
Voltage
समानांतर सर्किट में वोल्टेज सभी तत्वों के लिए समान होता है।

CUrrent
प्रत्येक विशिष्ट प्रतिरोधी में धारा Ohm's law द्वारा पाया जाता है।
Factoring out the voltage gives

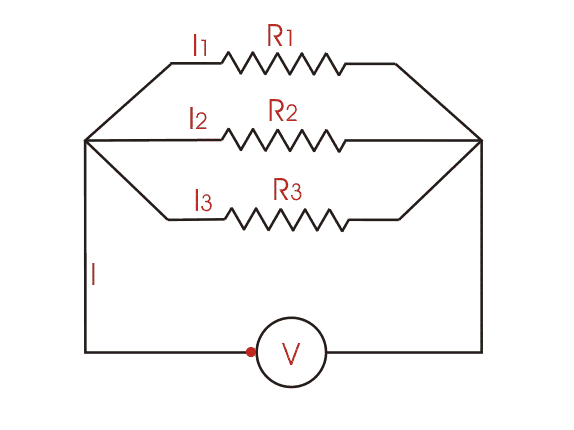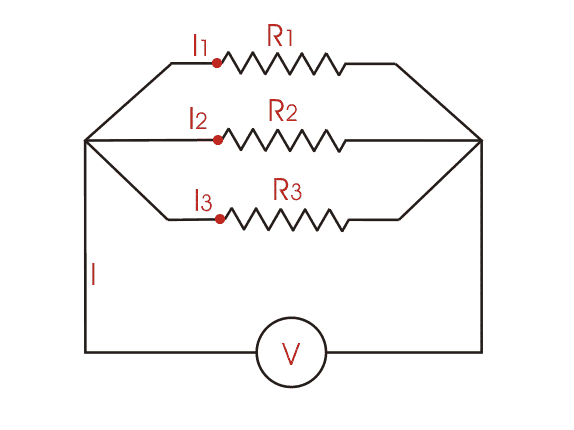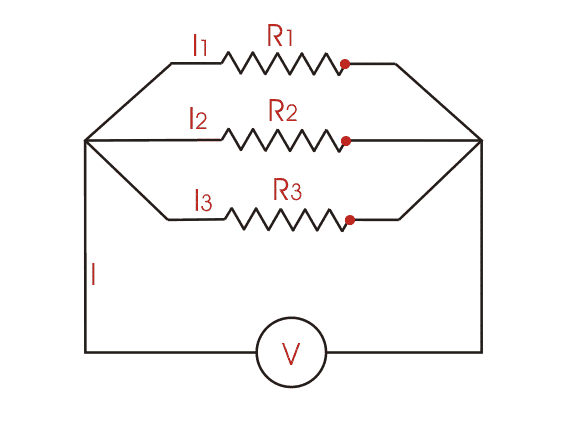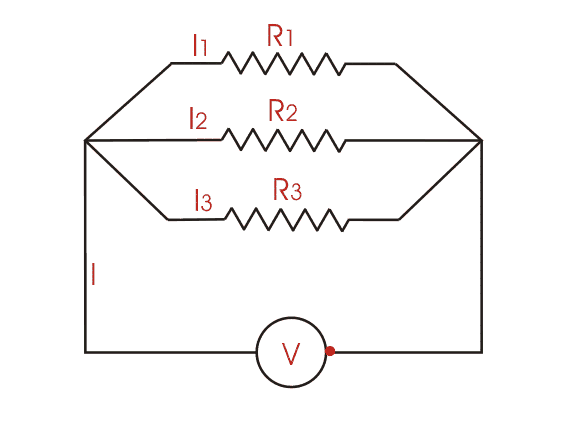
Resistors
To find the total resistance of all components, add the reciprocals of the resistances of each component and take the reciprocal of the sum. Total resistance will always be less than the value of the smallest resistance:

For only two resistors, the unreciprocated expression is reasonably simple:

Inductors
Inductors follow the same law, in that the total inductance of non-coupled inductors in parallel is equal to the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of their individual inductances:


Capacitors
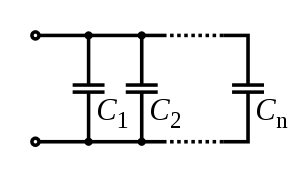
The total capacitance of capacitors in parallel is equal to the sum of their individual capacitances:

DIFFRENCE Btw. SERIES & PARALLEL CIRCUIT
|
Series Circuits
|
PARALLEL
CIRCUITS
|
|
All components share the same (equal)
current.
|
All components share the same (equal)
voltage.
|
|
Voltage drops add to equal total voltage.
|
Branch currents add to equal total current.
|
|
Resistances add to equal total resistance.
|
Resistances diminish to equal total
resistance.
|




Comments
Post a Comment